Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Taiki; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1112_1 - S1112_4, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kasai, Satoshi; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Hara, Hirotsugu*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1054_1 - S1054_4, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Kondoh, Takashi; Hayashi, Toshimitsu; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sugie, Tatsuo
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1111_1 - S1111_4, 2007/11
A diagnostic of fusion-generated alpha-particles is important to understand burning plasma physics, however, an effective measurement method has not yet been established. A collective Thomson scattering (CTS) diagnostic CO laser is being developed to establish a diagnostic method of confined alpha-particles. To realize the CTS diagnostic, a high-repetition Transversely Excited Atmospheric (TEA) CO
laser is being developed to establish a diagnostic method of confined alpha-particles. To realize the CTS diagnostic, a high-repetition Transversely Excited Atmospheric (TEA) CO has been developed. In order to obtain single-mode output, which is needed for the CTS diagnostic, seed laser is injected to the cavity with an unstable resonator. Using this technique, output energy of 17J with the frequency of 15 Hz has been achieved with single-mode output. These results gives a prospect for the CTS diagnostic on International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which requires energy of 20 J with the repetition rate of 40 Hz. Proof-of-principle test is being performed with the improved laser system on the JT-60U tokamak.
has been developed. In order to obtain single-mode output, which is needed for the CTS diagnostic, seed laser is injected to the cavity with an unstable resonator. Using this technique, output energy of 17J with the frequency of 15 Hz has been achieved with single-mode output. These results gives a prospect for the CTS diagnostic on International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which requires energy of 20 J with the repetition rate of 40 Hz. Proof-of-principle test is being performed with the improved laser system on the JT-60U tokamak.
Peterson, B. J.*; Konoshima, Shigeru; Kostryukov, A. Y.*; Seo, D. C.*; Liu, Y.*; Miroshnikov, I. V.*; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Parchamy, H.*; Kawashima, Hisato; Iwama, Naofumi*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1018_1 - S1018_4, 2007/11
An overview of the research and development of imaging bolometers giving a perspective on the applicability of this diagnostic to a fusion reactor is presented. Traditionally the total power lost from a high temperature has been measured using one dimensional arrays of resistive bolometers. The large number of signal wires associated with these resistive bolometers poses hazards not only at the vacuum interface, but also in the loss of electrical contacts that has been observed in the presence of fusion reactor levels of neutron flux. Infrared imaging video bolometers (IRVB), on the other hand, use the infrared radiation from the absorbing metal foil to transfer the signal through the vacuum interface and out from behind a neutron shield. The IRVB can provide hundreds of channels of bolometric signal in an image of the plasma radiation. Recently a prototype IRVB has been deployed on the JT-60U tokamak which demonstrates the ability of this diagnostic to operate in a reactor environment.
Liu, Y.*; Tamura, Naoki*; Peterson, B. J.*; Iwama, Naofumi*; Konoshima, Shigeru; LHD Experimental Group*; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1124_1 - S1124_4, 2007/11
Two improved tomographic algorithms, including a linear (Tikhonov-Phillips) and a nonlinear (maximum entropy) regularisation method, have been employed for multi-pixel bolometric measurements in order to get as much information as possible while keeping the assumptions to a minimum. The most important features of these improved methods are the capability of reconstructing radiation distributions without any symmetry assumptions, built-in smoothing, and useful reconstructions with relatively few detectors. Furthermore, the effects of finite detector size have been taken into account with a full three dimensional treatment of the detector geometry. The application of tomographic imaging was implemented to a two-array X-ray camera on the Large Helical Device (LHD) and a two-dimensional infrared imaging bolometric pinhole camera on JT-60U. Pertinent examples of the results are presented both to illustrate the analysis techniques and to demonstrate the wealth of physics which can be studied.
Araghy, H. P.*; Peterson, B. J.*; Hayashi, Hiromi*; Konoshima, Shigeru; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Seo, D. C.*; JT-60U Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1116_1 - S1116_4, 2007/11
We obtain the local foil properties of the JT-60U imaging bolometer foil (a single graphite-coated gold foil with an effective area of 9  7 cm
7 cm and a nominal thickness of 2.5 microns) such as the thermal diffusivity and the product of the thermal conductivity and the thickness of the foil by the foil calibration. Calibration of the foil was made in situ using a He-Ne laser (
and a nominal thickness of 2.5 microns) such as the thermal diffusivity and the product of the thermal conductivity and the thickness of the foil by the foil calibration. Calibration of the foil was made in situ using a He-Ne laser ( 27 mW) as a known radiation source to heat the foil. The thermal images of the foil are provided by an IR camera (micro-bolometer type). The parameters are determined by finite element modeling of the foil temperature and comparing the solution to the experimental results. In this work we apply this calibration technique to investigate the spatial variation of the foil parameters. Significant variation in the local temperature rise of the foil due to local heating by the laser beam indicates a spatial variation of the foil parameters. This variation is possibly due to nonuniformity in the carbon coating and/or the thickness of the foil. In a separate work, the spatial calibration data will be used to produce the bolometer intensity data to be utilized in the tomographic analyses.
27 mW) as a known radiation source to heat the foil. The thermal images of the foil are provided by an IR camera (micro-bolometer type). The parameters are determined by finite element modeling of the foil temperature and comparing the solution to the experimental results. In this work we apply this calibration technique to investigate the spatial variation of the foil parameters. Significant variation in the local temperature rise of the foil due to local heating by the laser beam indicates a spatial variation of the foil parameters. This variation is possibly due to nonuniformity in the carbon coating and/or the thickness of the foil. In a separate work, the spatial calibration data will be used to produce the bolometer intensity data to be utilized in the tomographic analyses.
Kobayashi, Shinji*; Yoshida, Maiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Sakata, Shinya; Kamada, Yutaka; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1049_1 - S1049_4, 2007/11
Real-time measurement system of the ion temperature profile has been developed for the feedback (FB) control of the ion temperature gradient (grad-
 ) with the filter charge exchange recombination spectroscopy (CXRS) system in JT-60U. The rapid analytical scheme without non-linear least square fitting enables us to calculate the ion temperature with four spatial points every 10 ms using a real-time processor system. The FB control experiment of grad-
) with the filter charge exchange recombination spectroscopy (CXRS) system in JT-60U. The rapid analytical scheme without non-linear least square fitting enables us to calculate the ion temperature with four spatial points every 10 ms using a real-time processor system. The FB control experiment of grad-
 has been demonstrated in ELMy H-mode plasmas by use of the neutral beam injectors having different deposition profiles as actuators. Grad-
has been demonstrated in ELMy H-mode plasmas by use of the neutral beam injectors having different deposition profiles as actuators. Grad-
 was controlled to the reference value in the ramp-down phase, however, it did not recovered in the ramp-up phase because the internal transport barrier or transport was affected by the ramp-down of grad-
was controlled to the reference value in the ramp-down phase, however, it did not recovered in the ramp-up phase because the internal transport barrier or transport was affected by the ramp-down of grad-
 . From the transient response analysis of grad-Ti, the increase in the central
. From the transient response analysis of grad-Ti, the increase in the central 
 using the additional heating was required to recover the deteriorated grad-
using the additional heating was required to recover the deteriorated grad-
 .
.
Sato, Masayasu; Isayama, Akihiko
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1029_1 - S1029_5, 2007/11
Using the extended Trubnikov's expression for the fully relativistic Maxwellian in the case of oblique propagation to the magnetic field (
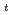 ), electron cyclotron emission (ECE) spectra are calculated in a high temperature (
), electron cyclotron emission (ECE) spectra are calculated in a high temperature (
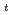 ) tokamak plasma. We investigate the ECE by changing the angles between the sight line and the equatorial plane or
) tokamak plasma. We investigate the ECE by changing the angles between the sight line and the equatorial plane or 
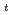 direction. Feature of ECE spectra can be interpreted from the viewpoints of relativistic, Doppler and absorption effects. The downshift frequency variation due to the relativistic effect in the high field side (HFS) observation is bigger than that in the low field side observation. Absorption at the HFS plasma results in the deep dip at the HFS of fundamental, second and third harmonics in the ECE spectra. For the vertical observation, in the case of optically thin case, ECE spectra are similar to the emissivity profile, and when electron density (
direction. Feature of ECE spectra can be interpreted from the viewpoints of relativistic, Doppler and absorption effects. The downshift frequency variation due to the relativistic effect in the high field side (HFS) observation is bigger than that in the low field side observation. Absorption at the HFS plasma results in the deep dip at the HFS of fundamental, second and third harmonics in the ECE spectra. For the vertical observation, in the case of optically thin case, ECE spectra are similar to the emissivity profile, and when electron density (
 ) is higher, ECE spectra are modified due to the absorption in plasma. Since the
) is higher, ECE spectra are modified due to the absorption in plasma. Since the 
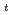 ,
, 
 ,
, 
 increase in the case of the SlimCS DEMO reactor, the ECE spectra expands to high frequency emission (2000 GHz). So, ECE detector in the case of Fourier transform spectrometer system should be modified from present liquid He cooled InSb detector because of the detection of high frequency emission.
increase in the case of the SlimCS DEMO reactor, the ECE spectra expands to high frequency emission (2000 GHz). So, ECE detector in the case of Fourier transform spectrometer system should be modified from present liquid He cooled InSb detector because of the detection of high frequency emission.
Fujimoto, Kayoko; Nakano, Tomohide; Kubo, Hirotaka; Sawada, Keiji*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Asakura, Nobuyuki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1121_1 - S1121_4, 2007/11
Understanding deuterium particle behavior in the divertor plasma is necessary to study the ionizing and recombining plasmas. Two-dimensional spectroscopic measurement of deuterium emission is useful to understand deuterium particle behavior in divertor plasmas. The information of the ionization and recombination can be obtained by measurement of deuterium Balmer-series lines. A wide-spectral-band spectrometer with a CCD detector was used to observe deuterium Balmer-series lines with two-dimensional spatial distribution in the JT-60U divertor region. From the measurement, we can obtain a two-dimensional distribution of D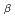 and D
and D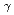 using a computer tomography technique. The D
using a computer tomography technique. The D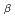 emission was strong above the strike point in the inner divertor and around the strike point in the outer divertor. The D
emission was strong above the strike point in the inner divertor and around the strike point in the outer divertor. The D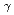 emission was strong above the strike point in the inner divertor.
emission was strong above the strike point in the inner divertor.
Kojima, Atsushi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Iguchi, Harukazu*; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1104_1 - S1104_4, 2007/11
A lithium ion gun is under construction for a lithium beam Zeeman polarimetry on JT-60U. The performance of the prototype ion gun has been estimated by the numerical simulation taking the space charge effects into account. The target values of the ion gun are the beam energy of 30 keV, the beam current of 10 mA and the beam divergence angle within 0.13 degrees. The low divergence is required for the geometry of the Zeeman polarimetry on JT-60U where the observation area is 6m away from the neutralizer. The simulation results show the beam loss of 50% caused by the clash to the electrode such as an cathode and the neutralizer. Moreover, the beam transport efficiency from the neutralizer to the observation area is low due to the broadening of the divergence angle. The total beam efficiency is about 5%. Extracted current profile affects the beam property and efficiency. The peaked profile achieves better efficiency than the hollow one. As a result, beam current of 1mA is obtained at the observation area by the simulation for the prototype ion gun.
Hatae, Takaki; Howard, J.*; Hirano, Yoichi*; Naito, Osamu; Nakatsuka, Masahiro*; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1026_1 - S1026_5, 2007/11
A high-throughput polarization interferometer is being developed to demonstrate for the first time the utility of Fourier transform spectroscopy for Thomson scattering diagnostics of high temperature plasma. Target 
 and
and 
 ranges for the prototype polarization interferometer are
ranges for the prototype polarization interferometer are  1 keV and
1 keV and  5
5 10
10 m
m , respectively. This paper describes the design of the polarization interferometer and the results of initial tests.
, respectively. This paper describes the design of the polarization interferometer and the results of initial tests.
Sato, Kazuyoshi; Omori, Junji; Ebisawa, Katsuyuki*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Neyatani, Yuzuru
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1088_1 - S1088_4, 2007/11
A part of diagnostic device in vacuum vessel is planned to install in the port plug to make sure the line of sight of diagnostics. Only basic concept is shown for the port plug since design of diagnostic devices has not been substantiated yet. The integration design of the port plug has been performed and the structure concept for electro-magnetic and neutron load has been investigated as for the No.11 upper port plug to confirm reliability of the proposed design. Three diagnostics will be installed in the No.11 upper port plug, the edge Thomson scattering system, the visible-IR TV divertor viewing system and the neutron activation system. To integrate theses diagnostic systems in the port plug, it was designed the arrangement of the labyrinth of optical path, the driving mechanism and cooling systems for shutters and mirrors, the maintenance space. The part just behind the blanket shield module (BSM) was changed to secure a space for maintenance and for associated diagnostic first mirror and shutter, whereas this place is assigned for neutron shielding in the present design. The BSM support, which is main component to apply the electro-magnetic load, was arranged with optical path inside BSM.
Ito, Naoki*; Mase, Atsushi*; Kogi, Yuichiro*; Seko, Noriaki; Tamada, Masao; Shen, Z.*; Yang, L.*; Domier, C. W.*; Luhmann, N. C. Jr.*; Sakata, Eiji*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 2, p.S1042_1 - S1042_4, 2007/11
As the importance of plasma imaging diagnostics increases, the fabrication of high performance millimeter-wave planar components becomes essential. This paper describes the development of high performance millimeter-wave planar components such as antennas and filters using low-loss fluorine substrate. The problems to be solved are low degree of adhesion between copper foil and fluorine substrate and shape of antenna pattern. In order to solve the problems, surface treatment of fluorine films and a fabrication method using Electro Fine Forming (EF2) are utilized.
Wang, F.*; Nakamura, Kazuo*; Mitarai, Osamu*; Kurihara, Kenichi; Kawamata, Yoichi; Sueoka, Michiharu; Sato, Konosuke*; Zushi, Hideki*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Yamaguchi, Taiki; Narushima, Yoshiro*; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Yuji*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; LHD Experimental Group*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English